We had previously reported on novel treatments for those suffering with treatment resistant depression (TRD). At the APA conference, Roger McIntyre MD presented on updates to TRD treatments:
- Childhood trauma can contribute to poor response to medications for depression.
-
Patients with high degree of loneliness have a higher chance of using NSAIDS, antidepressants, anxiolytics, benzodiazepines, opioids and polypharmacy.
-
Antidepressants have not increased in effectiveness since the 1980s, although the efficacy of placebo is increasing.
-
Treatment resistant depression metrics should also include the patient’s experience of quality of life.
How do inflammatory markers correlate with treatment resistant depression?
-
Obesity changes one’s biotype, like trauma, and creates an inflammatory picture.
-
Higher CRP, the less escitalopram works, and the more nortriptyline works.
-
Star-D taught us that 55% of people will meet state 2 treatment resistance.
-
Disturbances in cognition and reward are the strongest contributors of functional impairment.
-
Getting back to work might actually help your antidepressant.
Focus on the dopaminergic pathways, via prapipexole (a treatment typically for Parkinson’s disease).
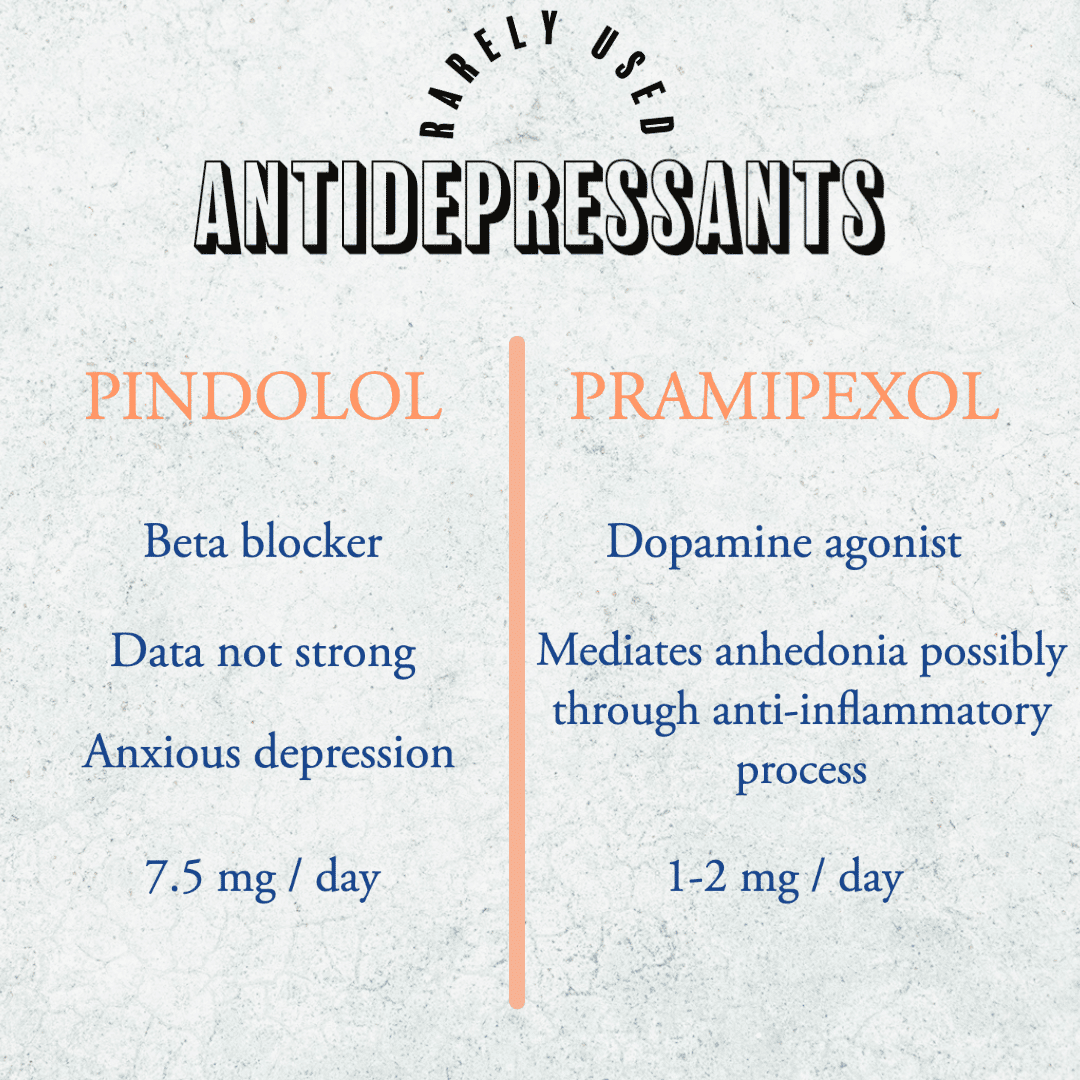
-
Vortioxetine and venlafaxine (150+) are the only two dose dependent medications, when reviewed on a group level.
-
Most popular strategy for add-on in TRD is to add a benzo which is NOT evidence based. The “right” answer is to add an atypical antipsychotic. Atypicals are especially good for rumination, which affects 40-80% of people with depression.
-
Add antidepressant (bupropion) vs atypical? Looking at the VAST-D study from 2017 in a VA population, aripiprazole was MORE effective than bupropion. Those who did well with aripiprazole were those with 4’s – anger, agitation, anxiety, and attentional disturbances.
If you are struggling with substance or alcohol use, depression, or anxiety, intensive outpatient may be right for you. Contact us at (888) 730-5220 or contact us to begin the process of healing today!
 Bruce Bassi
Bruce Bassi





